Transformer Bushing: Types, Parts, Functions, Working and Importance
Power transformers operate at very high voltage levels, where safety and insulation are extremely critical. One of the most important components that ensures safe electrical connection between internal windings and external circuits is the transformer bushing.
At TransformerGuruji.com, we explain transformer concepts in a simple, practical, and industry-friendly way. In this article, you will learn everything about transformer bushings, including their types, parts, functions, advantages, limitations, and importance in power transformers.
What Is a Transformer Bushing?
A transformer bushing is an insulated device that allows an electrical conductor to pass safely through the grounded transformer tank or enclosure without causing electrical leakage or a short circuit.
In simple words, a transformer bushing provides:
- Safe electrical insulation
- Strong mechanical support
- A controlled path for current flow
Transformer bushings are widely used in:
- Power transformers
- Distribution transformers
- Reactors
- Circuit breakers
- High-voltage electrical equipment
Depending on voltage rating and application, bushings are made from porcelain, composite material, oil-impregnated paper (OIP), or resin-impregnated paper (RIP).
Importance of Transformer Bushing
Without a transformer bushing, it is impossible to take high-voltage conductors out of the transformer tank safely. Bushings play a major role in transformer reliability and safety.
Why transformer bushings are important:
- Prevent electrical leakage and flashover
- Avoid short circuits between live and grounded parts
- Protect transformer oil and insulation system
- Increase transformer life and reliability
- Ensure safe power transmission
Due to these reasons, transformer bushings are considered critical safety components in power systems.
Main Functions of Transformer Bushing
1. Electrical Insulation
Transformer bushings separate live conductors from grounded parts like the transformer tank, preventing insulation failure and flashover.
2. Electrical Conduction
They provide a safe electrical connection between internal transformer windings and external circuits such as cables, busbars, or overhead lines.
3. Sealing Protection
Bushings are properly sealed to prevent moisture, dust, and air from entering the transformer, helping maintain oil and insulation quality.
4. Mechanical Support
They mechanically support the conductor and withstand vibration, thermal expansion, and fault conditions.
5. Heat Dissipation
High-voltage bushings may include cooling fins or oil circulation paths to reduce temperature rise during operation.
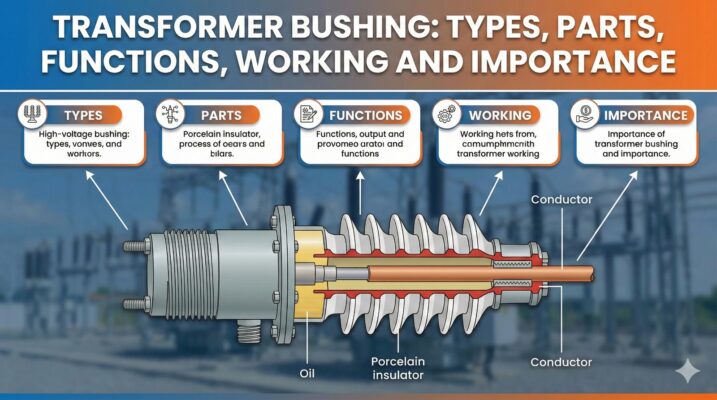
Main Parts of a Transformer Bushing
A transformer bushing consists of several components working together for safe operation:
1. Insulating Material
The main insulation body, usually made of porcelain, composite material, OIP, or RIP, depending on voltage and environment.
2. Insulating Sleeve
Provides additional insulation and environmental protection around the conductor.
3. Central Conductor
Carries current from transformer winding to the external circuit.
4. Terminal Connector
Located at the top, used to connect overhead lines, cables, or busbars.
5. Flange or Mounting Base
Fixes the bushing to the transformer tank and ensures proper sealing and mechanical strength.
6. Dielectric Medium (Oil or Resin)
Oil or resin improves insulation strength and heat dissipation.
7. Cooling Fins
Provided in high-voltage bushings to control temperature rise.
8. Sealing Arrangement
Prevents moisture and contamination ingress.
9. Grounding Arrangement
Improves safety and reduces electrical stress.
10. Voltage Tap (If provided)
Used for testing, monitoring, and diagnostic purposes.
Types of Transformer Bushings
Transformer bushings are classified based on construction, insulation type, and application.
1. Oil-Impregnated Paper (OIP) Bushings
- Paper insulation impregnated with mineral oil
- Used in oil-filled power transformers
- Suitable for high-voltage applications
2. Resin-Impregnated Paper (RIP) Bushings
- Paper insulation impregnated with epoxy resin
- No free oil inside
- Suitable for oil-filled and dry-type transformers
3. Composite Bushings
- Made from silicone rubber or epoxy
- Lightweight and pollution-resistant
- Ideal for coastal and industrial areas
4. Porcelain Bushings
- Traditional and widely used
- Excellent electrical and mechanical strength
- Common in outdoor substations
5. Condenser (Capacitance) Bushings
- Designed to control electric field stress
- Used in high-voltage transformers
- Allow condition monitoring
6. Dry-Type Bushings
- Used in dry-type transformers
- Suitable for indoor and eco-sensitive areas
7. Wall Bushings
- Used to pass conductors through transformer or substation walls
8. Low-Voltage Bushings
- Used for low-voltage transformer connections
9. High-Voltage Bushings
- Designed for 132 kV, 220 kV, 400 kV and above
- Handle very high electrical stress
Special Design Features of High-Voltage Transformer Bushings
For voltages 245 kV and above, bushings include special features such as:
- Arc shields to control electric stress
- Detachable bottom arc shields
- Oil-filled space between core and porcelain under vacuum
- Oil level sight glass on expansion bowl
- Top terminal for overhead line connection
- Optional arcing horns for extra protection
These features improve safety, reliability, and performance under extreme electrical stress.
Advantages of Transformer Bushings
- Safe connection of high-voltage conductors
- Reliable insulation and sealing
- Long service life
- Suitable for indoor and outdoor applications
- Improves overall transformer performance
Limitations of Transformer Bushings
- Sensitive to moisture ingress
- Requires periodic inspection and testing
- Bushing failure can cause serious transformer damage
FAQs – Transformer Bushing