Buchholz Relay in Transformer: Working Principle, Construction, Function and Importance
Power transformers are critical equipment in any electrical system, and even a small internal fault can lead to serious damage if not detected early. At TransformerGuruji.com, we focus on explaining such protection systems in simple and practical language for students, engineers, and industry professionals. To protect oil-filled transformers from such hidden faults, a simple yet highly effective device called the Buchholz relay is widely used. It provides early warning and fast tripping, helping improve transformer life and system reliability.
The Buchholz relay is an important safety device used in oil-filled power transformers. It helps detect internal faults at an early stage and protects the transformer from serious damage. When a fault occurs inside the transformer, the relay gives an alarm or trip signal, allowing timely action. Because of its simple design, reliable working, and low maintenance, the Buchholz relay is widely used in substations and power plants.
What Is a Buchholz Relay?
A Buchholz relay is a gas-operated protection relay installed in oil-filled transformers. It works by detecting:
- Gas produced due to internal faults
- Sudden movement of transformer oil
These signs indicate that something is wrong inside the transformer.
Where Is the Buchholz Relay Installed?
The Buchholz relay is installed in the oil pipe between the main tank and the conservator tank of the transformer.
This position helps because:
- Gas produced inside the transformer flows toward the conservator
- The gas passes through the relay first
- Sudden oil flow during major faults can be detected quickly
Since the relay is always in contact with oil, it continuously monitors transformer health.
Why Is Buchholz Relay Required in Transformers?
Oil-filled transformers face electrical and thermal stress during operation. Internal faults such as:
- Winding short circuit
- Insulation failure
- Overheating
- Core faults
cause the transformer oil to break down and produce gas.
Common gases include hydrogen, carbon monoxide, methane, and ethylene. If these faults are not detected early, they can lead to fire, explosion, or total transformer failure. The Buchholz relay helps prevent such damage.
Main Functions of Buchholz Relay
1. Gas Detection
Gas produced due to internal faults collects in the relay chamber, indicating a problem inside the transformer.
2. Alarm Operation
Small or slow-developing faults generate gas gradually. This causes the upper float to operate and activate the alarm circuit.
3. Trip Operation
Severe faults create sudden gas generation and fast oil movement. The relay operates the trip contact and disconnects the transformer from the supply.
4. Oil Flow Monitoring Modern Buchholz relays also detect sudden oil flow caused by major internal faults.
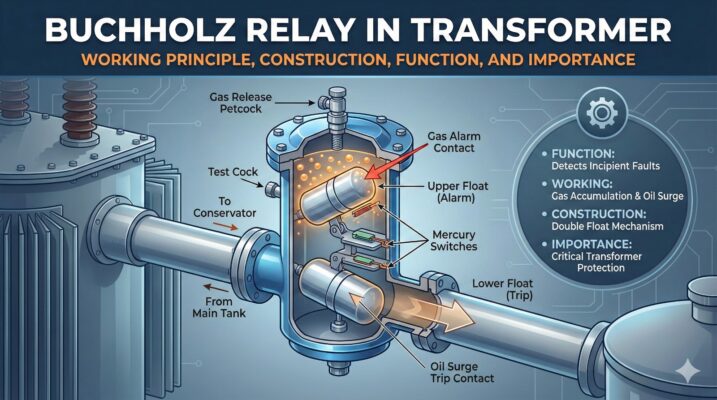
Construction of Buchholz Relay
The Buchholz relay has a simple and strong construction. Main parts include:
- Metal housing
- Gas collection chamber
- Upper and lower floats
- Mercury switch or micro switch
- Oil flow flap or vane (in modern types)
Float Functions
| Float Position | Operation |
| Upper float | Alarm signal |
| Lower float | Trip signal |
This simple construction makes the relay reliable and easy to maintain.
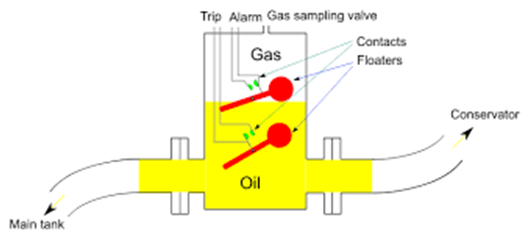
Working Principle of Buchholz Relay
The working of the Buchholz relay depends on gas formation and oil movement inside the transformer. It works under three conditions.
Normal Condition
- No gas formation
- Oil level remains normal
- Floats stay in position
- No alarm or trip signal
The transformer operates normally.
Minor Fault Condition (Alarm)
- Oil decomposes due to a small internal fault
- Gas enters the relay
- Oil level inside the relay drops
- Upper float moves up
- Alarm contact is activated
This warning allows maintenance before serious damage occurs.
Major Fault Condition (Trip)
- Large amount of gas is produced suddenly
- Oil flows rapidly through the relay
- Lower float or flap operates
- Trip circuit is activated
- Transformer is disconnected from supply
This action protects the transformer from severe damage.
Oil Flow Protection in Modern Buchholz Relays
Modern Buchholz relays include oil flow vanes or flaps. These devices detect sudden oil movement and operate the trip circuit faster, even before gas accumulation.
Gases Detected by Buchholz Relay
| Gas | Fault Indication |
| Hydrogen | Partial discharge |
| Carbon monoxide | Insulation overheating |
| Methane | Oil breakdown |
| Ethylene | High-temperature fault |
| Acetylene | Severe arcing |
These gases are analysed using Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) to identify the fault type.
Buchholz Relay and SCADA Systems
Modern Buchholz relays can be integrated with:
- SCADA systems
- Remote monitoring panels
- Alarm and event logging systems
This helps in quick fault detection and better transformer monitoring.
Advantages of Buchholz Relay
- Early fault detection
- No external power supply needed
- Simple and durable design
- Fast and reliable operation
- Improves transformer safety
Limitations of Buchholz Relay
- Used only in oil-filled transformers
- Not suitable for dry-type transformers
- Cannot detect external faults
- Slow oil leakage may not be detected
Conclusion
The Buchholz relay is a vital protection device for oil-filled transformers. Detecting gas formation and sudden oil movement gives early warning and fast tripping during internal faults. This helps prevent major damage, fire, and costly transformer failure. Due to its simple construction, reliable working, and proven performance, the Buchholz relay remains one of the most trusted transformer protection devices used in substations and power plants.