What Is Quality Management?
Quality management is the act of overseeing all activities and tasks that must be accomplished to maintain a desired level of excellence. It has four main components:
1. Quality planning
2. Quality assurance
3. Quality control
4. Quality improvement
1. Quality planning
Quality planning is implemented as a means of “developing the products, systems, and processes needed to meet or exceed customer expectations.”

PDCA/PDSA cycle is a continuous loop of planning, doing, checking (or studying), and acting. It provides a simple and effective approach for solving problems and managing change. The model is useful for testing improvement measures on a small scale before updating procedures and working practices
2. Quality assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is a way of preventing mistakes and defects in manufactured products and avoiding problems when delivering products or services to customers; which ISO 9000 defines as “part of quality management focused on providing confidence that quality requirements will be fulfilled“
the term “assurance” is often used as follows: Implementation of inspection and structured testing as a measure of quality assurance

Quality assurance includes two principles: “Fit for purpose” (the product should be suitable for the intended purpose); and “right first time” (mistakes should be eliminated). QA includes management of the quality of raw materials, assemblies, products and components, services related to production, and management
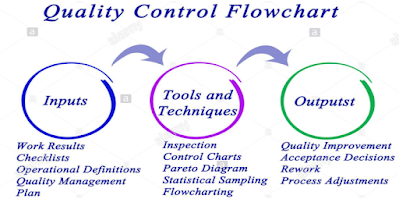
3. Quality Control
Quality control (QC) is a procedure or set of procedures intended to ensure that a manufactured product or performed service adheres to a defined set of quality criteria or meets the requirements of the client or customer. QC is similar to, but not identical with, quality assurance (QA). While QA refers to the confirmation that specified requirements have been met by a product or service, QC refers to the actual inspection of these elements.
QA is sometimes expressed together with QC as a single expression: quality assurance and control (QA/QC).
4. Quality Improvements
There are several different methods for quality improvement. They cover people-based improvement, process improvement, and product improvement
Seven simple tools can be used by any professional to ease the quality improvement process:
- Flowcharts,
- Check sheets,
- Pareto diagrams,
- Cause and effect diagrams,
- Histograms,
- Scatter diagrams,
- Control charts

